Model View Controller (MVC)
Description
The Model View Controller (MVC) pattern is one of the most commonly used software architecture patterns in web development. Many languages and frameworks, such as Ruby on Rails, Django, and Angular, use MVC as the basis for organizing code and separating concerns. The MVC pattern divides an application into three main components: the model, the view, and the controller. Each component has a specific role and interacts with the others in a well-defined way.
The MVC pattern separates the presentation layer and interactions with the user from the business logic and data storage. This separation of concerns makes it easier to maintain and extend the application over time. Here is a brief overview of each component in the MVC pattern:
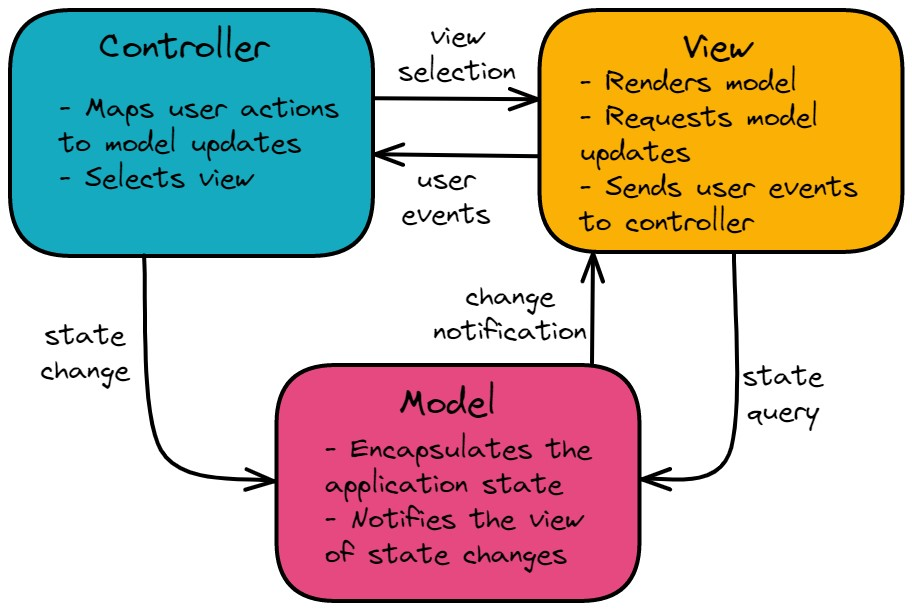
- Model: The model represents the data and business logic of the application. It is responsible for managing the state of the application, performing calculations, and interacting with the database. The model notifies the view and controller when changes occur, so they can update their state accordingly.
- View: The view is responsible for presenting the data to the user in a way that is easy to understand and interact with. It receives data from the model and displays it to the user.
- Controller: The controller acts as an intermediary between the model and the view. It receives input from the user, processes it, and updates the model and view accordingly. The controller is responsible for handling user interactions, such as clicking a button or submitting a form.
There are many minor variations of the MVC pattern depending on the resources and frameworks used. However, the core principles of separating concerns and organizing code into three main components remain the same.
Diagram
When to Use
The MVC pattern is well-suited for web applications that require a separation of concerns between the presentation layer and the business logic. It is especially useful for applications that need to be maintained and extended over time, as the separation of concerns makes it easier to add new features and fix bugs.
In general you should consider the MVC pattern when:
- There are multiple ways to view and interact with the data
- When future requirements for interacting with and presenting the data are unknown
- When there is an available framework that supports the MVC pattern
Advantages
The main advantages of the MVC pattern are:
- The data and its representation are separated, allowing them to change independently
- The same data can easily be presented in many different ways
Disadvantages
The main disadvantages of the MVC pattern are:
- The framework can be complex to navigate
- For simple data it introduces unnecessary complexity
- Lacks nuance for complex systems