Layered Architecture
Description
The Layered architecture pattern organizes the software into distinct layers, each with a specific responsibility. When implemented correctly, this pattern can improve maintainability, scalability, and testability of the software system. It can also allow for stronger security measures by isolating sensitive data and operations in separate layers.
The layers are typically organized in a hierarchical manner, with each layer providing services to the layer above it and consuming services from the layer below it. This separation of concerns helps to reduce complexity and allows for easier modification of individual layers without affecting the entire system.
Layers should never communicate directly with layers that are not adjacent to them. Instead, communication should be done through well-defined interfaces, which helps to decouple the layers and make the system more flexible. This separation also allows for the replacement of individual layers with minimal impact on the rest of the system.
Diagram
This simple diagram illustrates the concept of layered architecture using some common layers found in software systems:
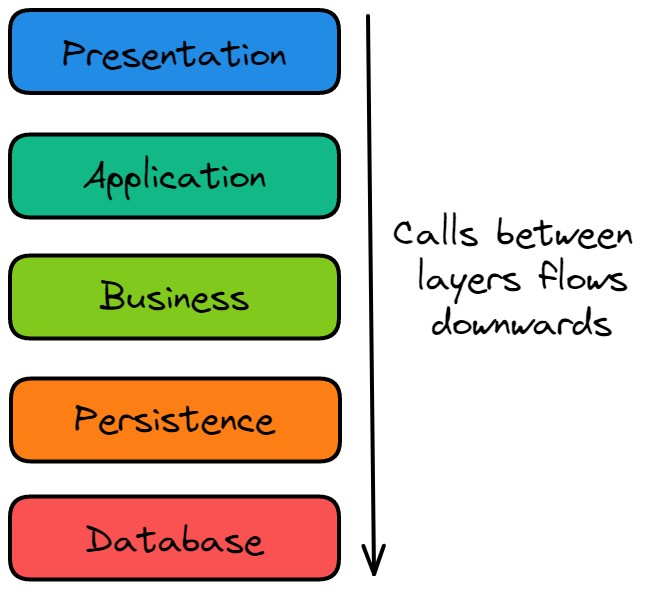
Each upper layer will call methods from the layer below it, and the lower layer will return the results to the upper layer.
When to Use
The layered architecture pattern is suitable for medium to large software systems where maintainability, scalability, and testability are important requirements. It is particularly useful when the system needs to be divided into distinct functional areas that can be developed and maintained independently.
You should consider a layered architecture when:
- You are adding functionality on top of an existing system.
- When the development team is large and needs to be divided into smaller groups where each can own a specific layer.
- When you need to replace or upgrade individual layers without affecting the rest of the system.
- When there is a requirement for multiple levels of security in the system.
Advantages
The main advantages of the layered architecture pattern include:
- Entire layers can be easily replaced as long as the interfaces remain the same..
- Authentication and authorization can be implemented at each layer, providing multiple levels of security.
Disadvantages
The layered architecture pattern also has some disadvantages, including:
- Cleanly separating the layers is often difficult, and in some cases, a high level layer may need to interact directly with a lower level layer.
- Performance can be impacted by the need to pass data between layers. Each layer adds overhead to the processing of requests.